Features of our framework
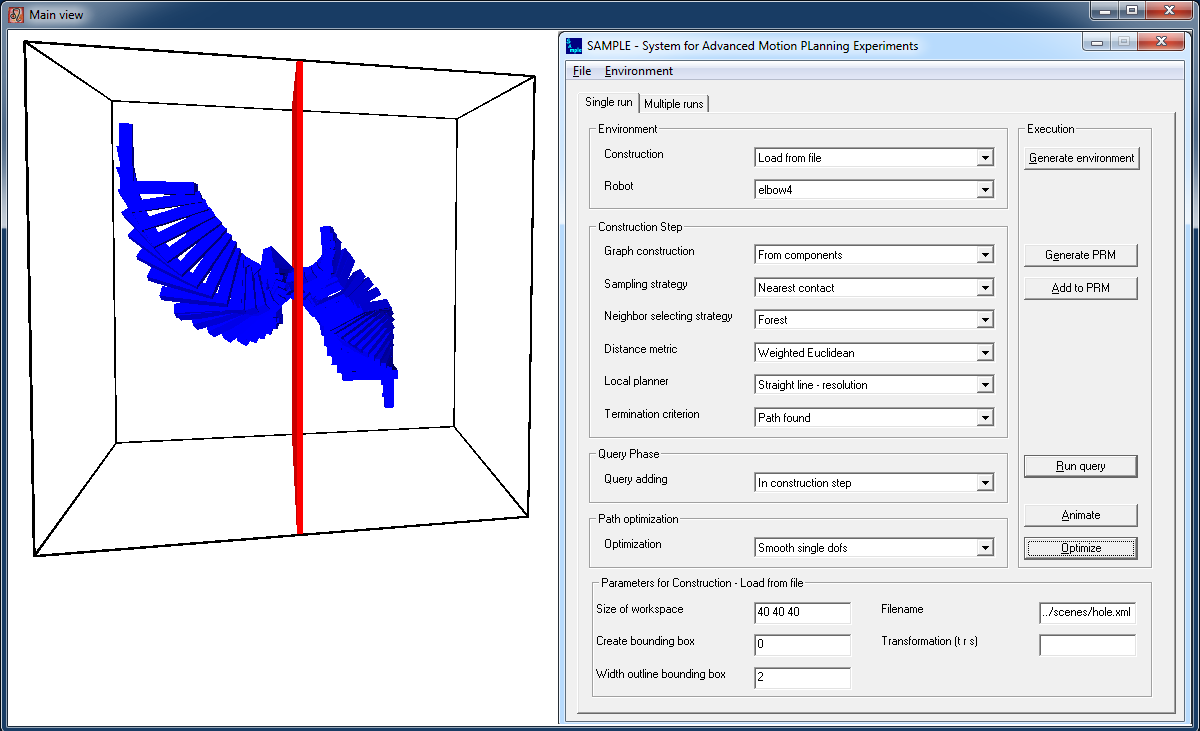
Specifying the PRM
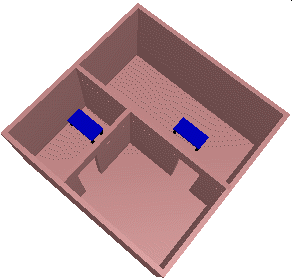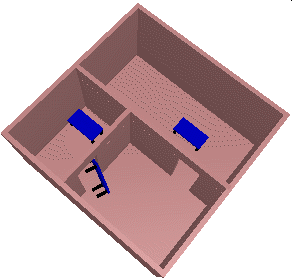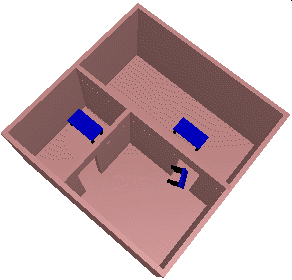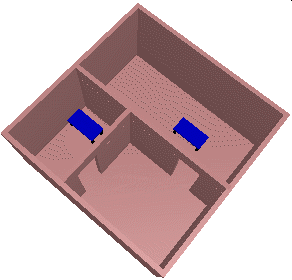
First, an environment and robot has to be chosen. They can be specified by any VRML file or by our own XML based file format.
At the moment, we support rigid body and articulated robots. Second, implementations for the construction step can be specified.
This includes a sampling strategy, neighbor selecting strategy, distance metric, local planner and termination criterion.
Then, the user can specify when the query (or queries) should be added to the roadmap.
Each query consists of a start and goal configuration. For each configuration, the user can specify the values for each degree
of freedom of the robot. Finally, a path that is extracted from the roadmap can be optimized by choosing a particular optimization strategy.
Experiments
After the implementation of the PRM has been specified, the user can set up the actual experiment. There are two types of experiments possible.
First, the user can compare different instances of a PRM component by selecting those instances. For example, the user has selected the Sampling component and has chosen the Bridge test, Gaussian and Medial axis sampling techniques.
Second, the user can examine the influence of a particular parameter of an instance. This can be done by specifying the range and step size of parameter. For example, in Figure 6, we want to know what happens when we change parameter sigma in the Gaussian sampling strategy. One (or more) experiment(s) are performed for each different value of sigma [1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0].
Finally, the user can specify how often the (set of) experiments have to be performed (by specifying the number of runs).
Statistics
Many kinds of charts for many different statistics can be generated. Because the statistical data is processed automatically, the chance on errors is reduced.