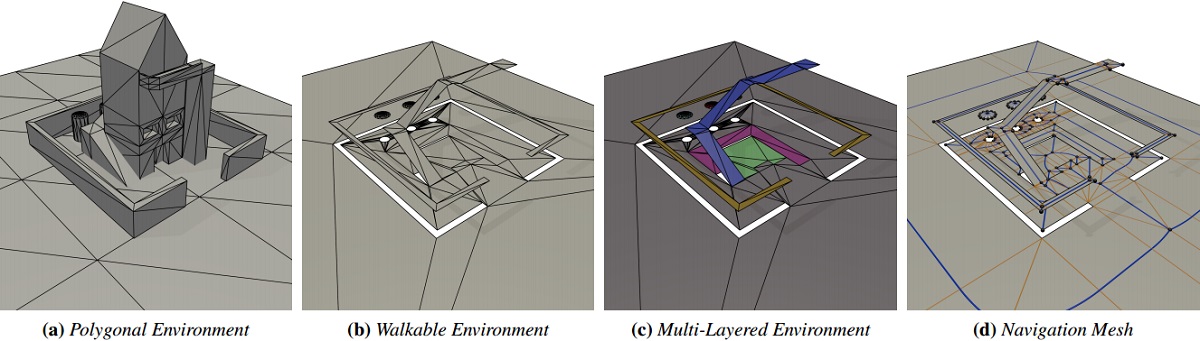
Abstract
A multi-layered environment (MLE) is a representation of the walkable environment (WE) in a 3D virtual environment that comprises a set of two-dimensional layers together with the locations where the different layers touch, which are called connections. This representation can be used for crowd simulations, e.g. to determine evacuation times in complex buildings, or for finding the shortest routes. The running times of these algorithms depend on the number of connections.
Finding an environment with the smallest number of connections, is an NP-Hard problem. Our first algorithm tackles this problem by using an integer linear program which is capable of finding the best possible solution, but naturally takes a long time. Hence, we provide two heuristics that search for MLEs with a low number of connections. One algorithm uses local search to gradually improve the found solution. The other one, called the height heuristic, is very fast and gives good solutions in practical environments
Reference
-
Arne Hillebrand, Marjan van den Akker, Roland Geraerts and Han Hoogeveen. Separating a Walkable Environment into Layers. In 9th International ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Motion in Games, pp. 101-106, 2016 (San Francisco, USA).
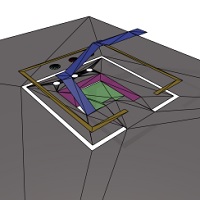
We researched its theoretical foundation in the paper Performing Multicut on Walkable Environments.
Some results
We used the following test environments in our paper, together with their obtained Multi-layered environments (MLEs). These MLEs were obtained using the height heuristic.
Each layer of an environment is shown in a different color.
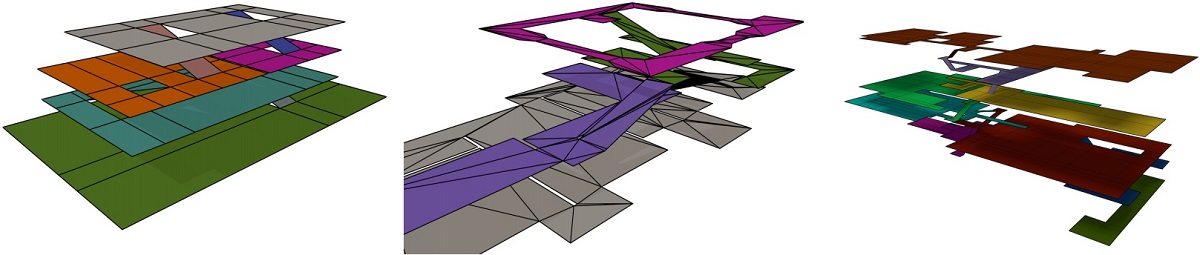
Parking lot, Halo and Library environments.
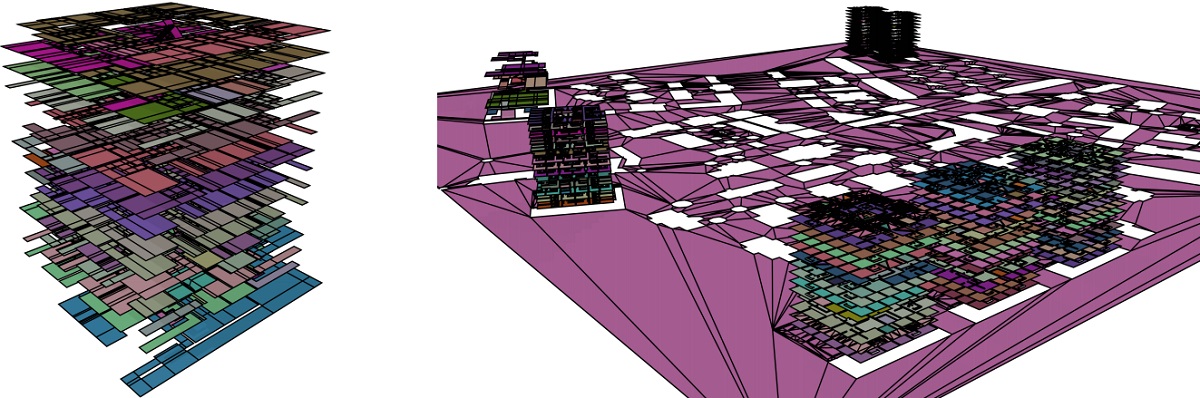
Tower and City environments.
More results can be found in our comparative study of navigation meshes.